The Oracle UPPER() function converts all letters in a string to uppercase.
Syntax #
The following illustrates the syntax of the Oracle UPPER() function:
UPPER(string)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Arguments #
The UPPER() function takes one argument:
1) string
is the string which is converted to uppercase
Return value #
The UPPER() function returns a string with all letters in uppercase.
Examples #
The following statement converts the string 'string function' to uppercase:
SELECT
UPPER( 'string functions' )
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the result:
'STRING FUNCTIONS'Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Let’s see the contacts table in the sample database:
The following statement groups contacts by their initials and returns the number of contacts for each alphabet.
SELECT
UPPER(SUBSTR (first_name, 1, 1)) initials,
COUNT(*)
FROM
contacts
GROUP BY
UPPER(SUBSTR (first_name, 1, 1))
ORDER BY
initialsCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
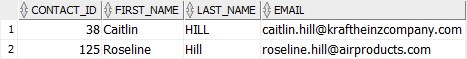
You can use the UPPER() function to perform case insensitive search for values in a column. To demonstrate this, let’s update the last name of the contact id 38 from Hill to HILL:
UPDATE contacts
SET
last_name = 'HILL'
WHERE
contact_id = 38;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To find contacts whose last name is Hill, HILL, or hill, you use the UPPER() function in the WHERE clause as follows:
SELECT
contact_id,
first_name,
last_name,
email
FROM
contacts
WHERE
UPPER(last_name) = 'HILL';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
Summary #
- Use the Oracle
UPPER()function to convert all letters of a string to uppercase.